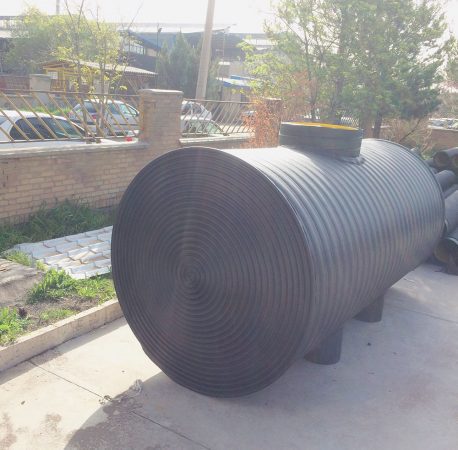
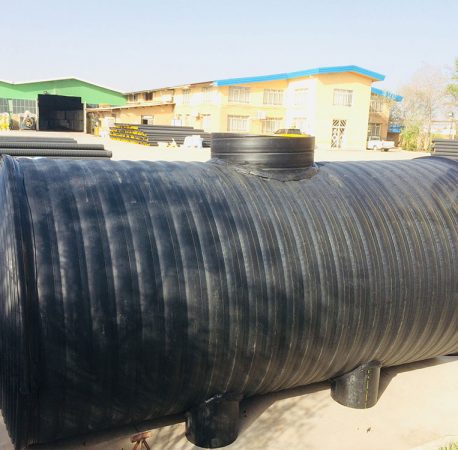
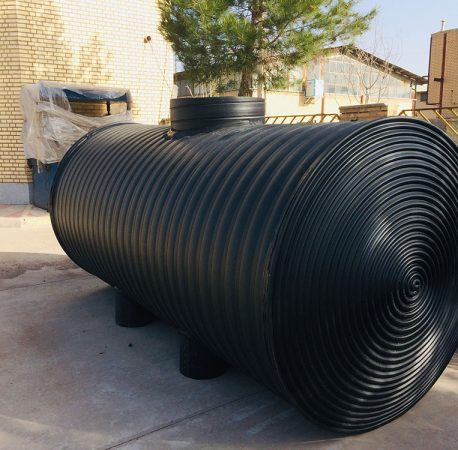
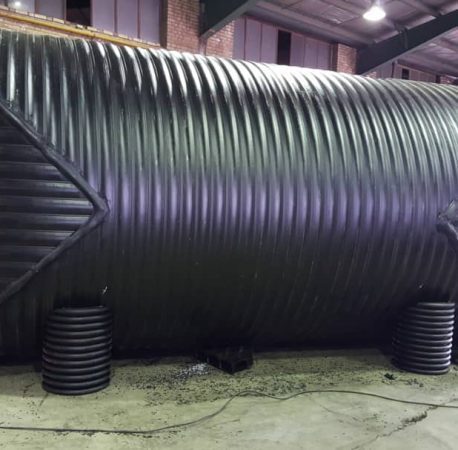
septic tank
- خانه
- septic tank
septic tank
The septic tank is one of the basic units of the wastewater treatment process after its production, which is the most important function of creating suitable conditions for settling and collecting suspended solids downwards and floating oily materials and foam towards the surface of the wastewater. Depending on the type of wastewater and the amount of treatment allowed, septic tanks have different capacities and different components. Therefore, the units in this tank can include sedimentation, flotation, anaerobic treatment, aerobic treatment, digestion and sludge collection.
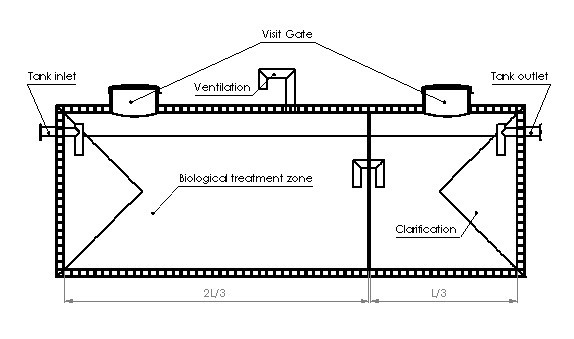
According to the following figure, the septic tank consists of the following components:
1- Sewage inlet system: includes pipe and inlet baffle.
2. The initial tank of the septic tank: which has the largest volume of the septic tank and usually the total volume of the septic tank is related to this section.
3- Separating wall: which prevents sludge, grease and floating oils from entering the clarification tank.
4. Clarification tank: This tank component contains almost the entire volume of the septic tank and accumulates wastewater free of sediment and floating materials.
5. Biogas outlet (ventilation): Through this duct, the gases produced due to anaerobic wastewater treatment processes, which are mainly methane, are released from these tanks.
6- Sewage outlet system: includes baffle and septic tank outlet pipe.
Product details
The primary goal in designing and determining the capacity of a septic tank is to provide suitable conditions for the removal of suspended solids and floating materials such as oil and foam. In this regard, in proportion to the inflow and per capita flow of wastewater production, having a smooth flow and wastewater retention time between 6 to 24 hours, are important parameters in designing the capacity of this type of reservoirs. According to the existing standards, two methods can be used to determine the capacity of the septic tank.
Determining the capacity by using the number of rooms in the complex, which is suitable for wastewater production per capita up to 6 cubic meters per day, and according to the table below is obtained.
( EPA, Design manual )
Number of rooms | Tank capacity (cubic meters) |
1 | 3 |
2 | 3 |
3 | 4 |
4 | 5 |
5 | 6 |
6 | 6 |
7 | 7 |
8 | 8 |
This method is suitable for capacities higher than 6 cubic meters per day. In this method, according to BS6297 standard, the capacity of this type of tanks is obtained from the following formula.
V = 2000 + (P × C)
In this regard, V is the capacity of the tank in liters, C is the per capita wastewater production per day in terms of liters, and P is the number of people in the complex.
The table below shows the per capita wastewater production for different locations.
Row | Location | the unit | Range | Normal amount | ||
Liters per day | ||||||
1 | Urban housing units | person | 150-250 | 200 | ||
2 | Recreational villas | person | 120-400 | 300 | ||
3 | Office buildings | 8-hour staff | 35-75 | 55 | ||
24-hour staff | 70-100 | 90 | ||||
4 | Factories and industrial workshops | 8-hour worker | 40-80 | 75 | ||
8-hour worker with bath | 100-150 | 120 | ||||
5 | Construction workshops | 8-hour staff | 40-80 | 60 | ||
24-hour staff | 80-120 | 100 | ||||
6 | Public Restroom | People (without flash tank) | 5-12 | 7 | ||
People (with flash tank | 12-20 | 15 | ||||
Removal of contaminants in wastewater, especially harmful organic matter, suspended solids and oil and floating foam on it, including the use of septic tanks for a proper pre-treatment before final treatment and transfer to the main treatment site. Among the important wastewater pollution parameters are BOD5, COD, TKN and TSS, the table below shows the removal rate of each of them.
row | Parameter | Inlet concentration to septic tank | Outlet concentration from septic tank | ||
(mg/lit) | (mg/lit) | ||||
1 | BOD5 | 165-296 | 135-227 | ||
2 | COD | 550-700 | 257-335 | ||
3 | TSS | 165-370 | 50-150 | ||
4 | TKN | 35-98 | 35-70 | ||
5 | Oil&Grease | 70-105 | 35-40 |
Request product advice









